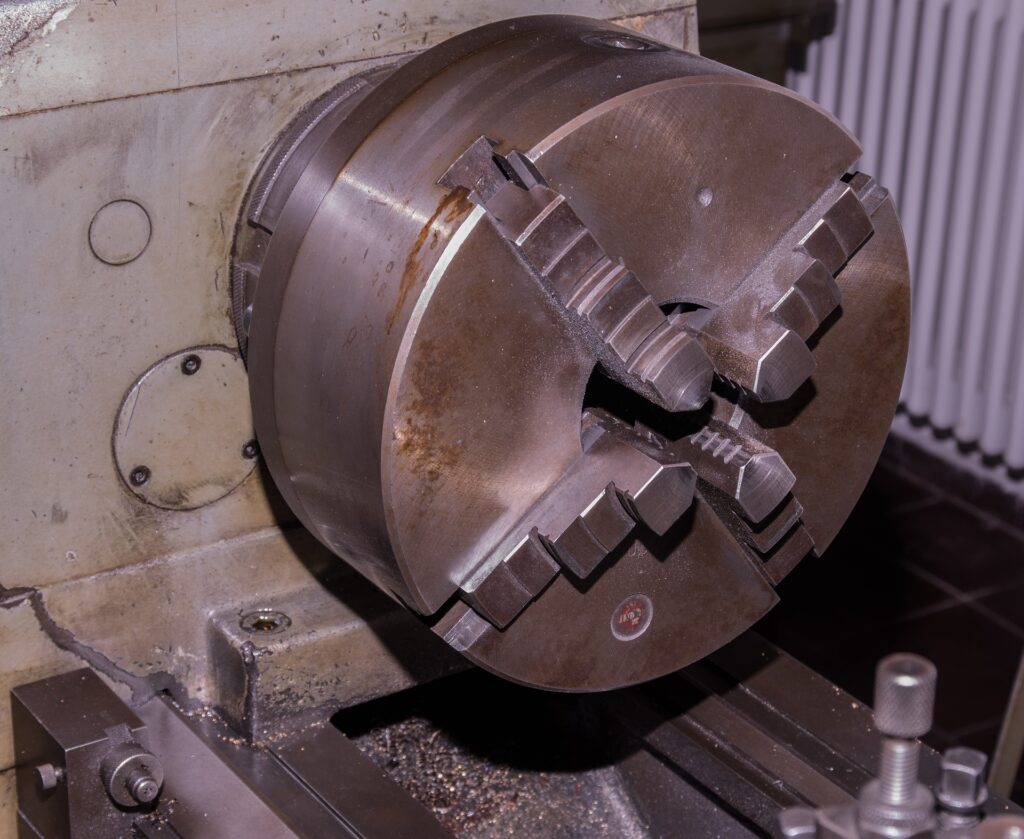
The Lathe is a material removing device used for turning round stock down to size.
The lathe is used to create threads on the outside of a round part, usually at the end of the work piece.
It is possible to thread the inside of a work piece with special cutting tools. .
It is also possible to round the edges of a work piece with special tools.
There are two types of lathes manual lathes and CNC lathes.
CNC lathes can shape a round work piece through the use of contours that are programmed into the CNC lathe by using G-Code.
CNC lathes can make many different types of complicated curved shapes very easily.
CNC lathe programs are usually created using CAM software.
Manual lathes are commonly used in the shop.
Another function lathes are used for is knurling round parts.
Calipers are good for checking the diameter of a work piece when it is being lathed.
Oil can be used as a lubricant when turning a work piece to reduce friction.
It is important to take into consideration the speeds and feeds when turning parts on a lathe.
Cutting speed is the rate at which the tool travels around the work piece in one revolution.
The feed rate is the rate at which the tool progresses along the length of the work piece.
The depth of cut is the depth of the chip taken from the work piece, the depth of the cut of the work piece is one half the diameter of the material that has been removed.
The parts of the lathe
The main parts of the lathe are the headstock, the tailstock, the bed, the carriage, and the quick-change gearbox.
The headstock is located on the left side of the bed.
The headstock spindle provides the drive for the fixtures (a collet or a chuck), that hold the parts, and consists of a single hollow cylindrical shaft, that is supported by bearings, a motor that geared provides the drive for turning the fixture. The headstock spindle can be driven by pulleys and a belt or by transmission gears.
The quick-change gearbox contains various sized gears that will provide the drive for the feed rod and the leadscrew which also provide a number of speeds for turning and thread cutting operations.
The leadscrew uses a split-nut when it is engaged by the split-nut lever it advances the carriage for thread cutting operations.
The carriage consists of three different components the saddle, the cross slide, and the apron. The cross slide is mounted on top of the saddle, the cross-slide provides the vertical cutting tool, either automatic or manual, vertical movement. Th cutting tool is held by the compound rest which is mounted on top of the cross slide.
The tailstock consists of the upper and lower tail stock castings, which can be adjusted for parallel or tapered turning of the work piece. The tailstock is locked into place by the tailstock clamp. The tailstock spindle has taper on its inner surface to hold the dead center. The tail stock spindle is held in a fixed position by a spindle clamp. The tailstock spindle can be moved in or out by the use of the tailstock handwheel, the tailstock handwheel can be used as a hand feed for drilling and reaming of the work piece.
Holding work pieces in the lathe
The work piece is held by a chuck or a collet at one end and the center holds the work piece at the other end.
Lathe safety
• Always wear the appropriate safety glasses.
• Roll up sleeves and remove neck ties, and tuck in loose clothing. Wear short sleeves when possible.
• Remove all jewelry before operating the lathe. • Never operate the lath without fully understanding all of its controls.
• Always make the safety guards are set up properly.
• Stop the lathe when measuring the size of the machined work piece or oiling the work piece.
• Never use a rag to clean a work piece when the lathe is running.
• Never try to stop the chuck or drive plate by hand.
• Make sure the face plate or chuck are mounted securely before starting the lathe.
• Always remove the chuck wrench before starting the lathe.